What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?
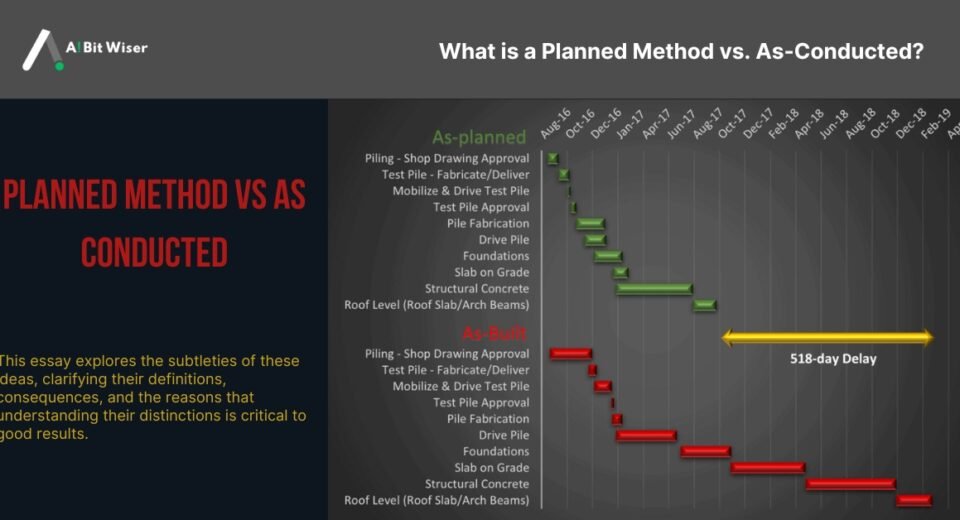
Knowing the difference between a “what is a planned method vs as conducted method?” is essential for assessing a process’s efficacy and correctness in the fields of research and project management. These terminologies aid in distinguishing between a project or study’s theoretical design and its actual implementation and execution. This essay explores the subtleties of these ideas, clarifying their definitions, consequences, and the reasons that understanding their distinctions is critical to good results. Defining the Planned Method A “planned method” is a method or strategy that is carefully thought out and prepared before a project or research endeavor is started. This approach is a perfected recipe that was developed using recognized best practices, theoretical models, and expected results. The planned approach is essentially a comprehensive road map that outlines the optimal course of action for a certain activity, research, or project. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” In research, the planned approach includes the project design, hypothesis development, instrument and methodology selection, and protocol creation for data collection and analysis. Usually outlined in research proposals or project plans, this strategy seeks to guarantee a methodical and regulated implementation. A planned method’s main goal is to offer an organized framework that increases the possibility of getting the intended outcomes. Following a carefully thought-out strategy guarantees validity, consistency, and dependability. It also makes stakeholder communication easier and provides a standard against which to measure the process’s efficacy. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Understanding the As-Conducted Method On the other hand, the “as-conducted method” deals with the real-time execution and implementation of a project or research. It incorporates the changes, additions, and departures from the original design that occur in real life. The as-conducted approach provides an overview of the project’s or study’s practical advancement, taking into account the dynamics and constraints that arise during implementation. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” The as-conducted approach encapsulates the main points of what happened, emphasizing any variations from the intended approach brought about by unanticipated difficulties, real-world limitations, or changing conditions. For instance, in a research project, researchers may modify their strategy in real-time to meet unforeseen problems that occur with data gathering technologies. This adaptability is essential for negotiating real-world situations and guaranteeing the project’s continuation despite departures from the initial plan. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Comparing Planned Method and As-Conducted Method A project or study’s overall efficacy and accuracy must be understood by comparing the planned and as-conducted methodologies. The as-conducted technique represents the real-world application and practical implementation, whereas the planned method sets objectives and offers a theoretical foundation. Analyzing these factors might provide insightful information on the effectiveness and success of the study or project. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Following the intended procedure is one important area of comparison. This entails assessing the degree to which the original plan and its actual implementation coincide. High adherence indicates successful planning and execution and shows that the project or research is moving along as planned. Deviations from the plan, however, are not always bad; they might indicate that essential modifications were made in reaction to unforeseen circumstances. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” The requirement for adaptations and flexibility is another crucial element, as the as-conducted technique makes clear. Although the planned technique offers an organized approach, it might not take into consideration every potential variable or unanticipated problem. The ability to modify the approach in response to real-world difficulties shows resiliency and aptitude for addressing issues. Analyzing these changes aids in determining the strength of the initial plan as well as the efficacy of the changes made during implementation. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Assessment of results is also essential. It entails contrasting the end outcomes with the initial goals specified in the strategy. Substantial changes from the original design may affect the final results and how they are interpreted. Comprehending these disparities is crucial for assessing the accomplishments and reliability of the undertaking or investigation and arriving at well-informed conclusions. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” The Importance of Recognizing the Difference It’s important to understand the differences between planned and as-conducted techniques for a number of reasons. It first helps in assessing how well the planning process was. Organizations and academics are able to determine the advantages and disadvantages of their planning techniques by analyzing the degree to which the plan is followed in practice. This knowledge may help with future planning and implementation. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Second, evaluating the effects of modifications and deviations aids in evaluating the team’s flexibility and problem-solving abilities. Unexpected obstacles are a common part of research projects, and successfully navigating these obstacles is essential to success. Knowing the as-conducted technique offers information regarding the team’s adaptability to these difficulties and the potency of their responses. Third, understanding the as-conducted approach provides a more realistic portrayal of the project’s or study’s results. Through an examination of the variations between the intended and implemented procedures, interested parties can get knowledge about the elements impacting the outcomes. This analysis enables a more thorough assessment of the project’s or study’s viability and success, directing future choices and advancements. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” Case Studies Illustrating Planned vs. As-Conducted Methods Examine a few case studies from various disciplines to demonstrate the ideas of planned and as-conducted techniques. What is a Planned Method vs As Conducted?” In clinical research, a particular protocol for therapy administration and outcome measurement may be part of the intended technique. However, problems like participant non-compliance or equipment faults might arise during the study. The difficulties encountered and the modifications made—such as modifying the course of treatment or adding more steps to deal with non-compliance—would be recorded using the as-conducted approach. Evaluating the variations between the intended and actual techniques aids in determining the validity and dependability of the research. What is a Planned